I. Introduction
Cybersecurity cases have become increasingly common in law in recent years, with hackers and cybercriminals targeting individuals, businesses, and government agencies. To combat these threats, law enforcement agencies are turning to artificial intelligence (AI) and big data projects to help solve these cases. In this article, we will explore the use of AI and big data in cybersecurity cases in law, and how machine learning approaches can be applied to these cases.
A. Brief Overview of Cybersecurity Cases in Law
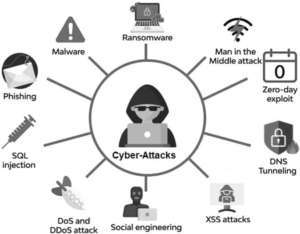
Cybersecurity cases in law refer to legal disputes related to cybersecurity, such as data breaches, cyber attacks, and cybercrime. These cases often involve complex technical issues, and it can be challenging to identify and prosecute the individuals responsible for these attacks. As the number of cyber attacks continues to rise, there is a growing need for innovative solutions to help solve these cases.
B. Importance of Using AI and Big Data in Solving Cybersecurity Cases
AI and big data projects can help law enforcement agencies to identify patterns and anomalies in large amounts of data that might otherwise be difficult to detect. Machine learning algorithms can learn from data to improve their accuracy and speed, which can be critical in identifying and preventing cyber attacks. Additionally, big data projects can help to identify patterns and trends that might be missed by traditional analytical methods, leading to more effective decision-making.
II. Understanding Machine Learning in Cybersecurity
A. Definition of Machine Learning
Machine learning is a subfield of AI that involves teaching computers to learn from data without being explicitly programmed. In cybersecurity, machine learning algorithms can be used to identify patterns and anomalies in data that might be indicative of a cyber attack. These algorithms can learn from past data to improve their accuracy and identify potential threats in real-time.
B. Machine Learning Techniques Used in Cybersecurity
There are several machine learning techniques that can be used in cybersecurity, including supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. Supervised learning involves training a machine learning algorithm on a labeled dataset, where the desired output is known. Unsupervised learning involves training a machine learning algorithm on an unlabeled dataset, where the desired output is not known. Reinforcement learning involves training a machine learning algorithm to take actions in an environment to maximize a reward.
C. Advantages of Using Machine Learning in Cybersecurity Cases
Machine learning algorithms can help to automate the process of identifying potential threats, which can save time and resources for law enforcement agencies. Additionally, machine learning algorithms can identify patterns and anomalies that might be missed by traditional analytical methods, leading to more effective decision-making. Finally, machine learning algorithms can learn from past data to improve their accuracy over time, leading to more accurate and effective cybersecurity solutions.
III. Big Data in Cybersecurity
A. Definition of Big Data
Big data refers to large and complex datasets that are difficult to analyze using traditional analytical methods. In cybersecurity, big data can refer to large amounts of network traffic data, log files, and other data sources that might be indicative of a cyber attack.
B. Applications of Big Data in Cybersecurity
Big data can be used in cybersecurity to identify patterns and trends that might be indicative of a cyber attack. Additionally, big data can be used to monitor network traffic and identify anomalies that might be indicative of a cyber attack. Finally, big data can be used to identify potential vulnerabilities in a system and develop strategies to mitigate these vulnerabilities.
C. Advantages of Using Big Data in Cybersecurity Cases
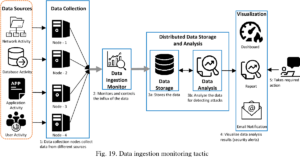
Big data projects can help law enforcement agencies to identify patterns and trends that might be missed by traditional analytical methods. Additionally, big data projects can process large amounts of data in real-time, allowing for faster detection and response to cyber threats. Here are some specific advantages of using big data in cybersecurity cases:
- Improved threat detection: Big data projects can analyze massive amounts of data from various sources to identify patterns and anomalies that may indicate a cyber attack. By analyzing network traffic, user behavior, and other data, big data tools can identify suspicious activity that may have been missed by traditional security tools.
- Better risk assessment: By processing large amounts of data, big data projects can identify potential vulnerabilities and weaknesses in an organization’s cybersecurity posture. This can help organizations prioritize their security efforts and allocate resources where they are needed most.
- Faster incident response: Big data projects can help organizations respond quickly to cyber incidents by providing real-time alerts and automated responses. This can help organizations contain an attack before it causes significant damage.
- Enhanced forensics: Big data projects can help investigators analyze large volumes of data from different sources to reconstruct cyber attacks and identify the perpetrators. By correlating data from different sources, big data tools can provide a more complete picture of an attack, which can help investigators identify the root cause and prevent future incidents.
Overall, big data projects can significantly improve an organization’s ability to detect, prevent, and respond to cyber threats. By combining big data with machine learning techniques, law enforcement agencies can develop more effective cybersecurity strategies and protect against increasingly sophisticated attacks.
IV. Case Studies: Examples of Cybersecurity Cases Solved Using Machine Learning and Big Data Projects
To better understand how machine learning and big data projects can help solve cybersecurity cases, let’s examine some examples:
- Cybersecurity Case 1: Malware Detection In this case, a law enforcement agency used a big data project to detect malware on a large network. The big data project analyzed network traffic logs and identified patterns that indicated the presence of malware. The project then used machine learning algorithms to classify the malware and develop a signature that could be used to detect similar malware in the future. As a result, the law enforcement agency was able to remove the malware and prevent further damage.
- Cybersecurity Case 2: Insider Threat Detection In this case, a company used a big data project to detect insider threats. The project analyzed data from various sources, including employee email and network activity logs, to identify patterns of behavior that may indicate an insider threat. The project used machine learning algorithms to identify anomalous behavior, such as an employee accessing sensitive data outside of normal business hours. By detecting insider threats early, the company was able to prevent data breaches and protect sensitive information.
- Cybersecurity Case 3: Fraud Detection In this case, a financial institution used a big data project to detect fraud. The project analyzed customer transaction data to identify patterns that may indicate fraudulent activity. The project used machine learning algorithms to identify anomalous behavior, such as a customer making multiple large transactions in a short period of time. By detecting fraud early, the financial institution was able to prevent financial losses and protect customer accounts.
These examples demonstrate how machine learning and big data projects can help solve cybersecurity cases in law enforcement. By analyzing large amounts of data and identifying patterns and anomalies, these projects can help detect cyber threats early and prevent further damage.
V. Ethical Considerations in Using AI and Big Data in Cybersecurity Cases
While the use of machine learning and big data projects can provide significant benefits for solving cybersecurity cases, there are also ethical considerations that must be addressed. Here are some potential issues to consider:
- Biases in machine learning algorithms: Machine learning algorithms may be biased based on the data they are trained on. For example, if a machine learning algorithm is trained on data that is biased against a particular group, it may produce biased results. It is important to ensure that machine learning algorithms are trained on unbiased data and that the algorithms are regularly reviewed for biases.
- Privacy concerns with the use of big data: The use of big data in cybersecurity cases may involve the collection and analysis of large amounts of personal data. This raises privacy concerns, particularly if the data is not adequately protected or if it is used for purposes beyond what it was originally collected for. Law enforcement agencies must ensure that they are collecting and using personal data in a lawful and ethical manner.
- Legal and ethical frameworks for the use of AI and big data in cybersecurity cases: There is a need for legal and ethical frameworks to guide the use of AI and big data in cybersecurity cases. These frameworks should outline the acceptable uses of these technologies, as well as the safeguards that must be in place to protect individuals’ rights and privacy.
VI. Future Directions in Using AI and Big Data in Cybersecurity Cases
The use of AI and big data in cybersecurity cases is an ever-evolving field. Here are some potential future directions and developments:
- Emerging technologies and techniques: There are many emerging technologies and techniques that could be applied to cybersecurity cases. For example, natural language processing and sentiment analysis could be used to analyze social media data for potential threats.
- Potential applications in law enforcement and national security: The use of AI and big data projects has potential applications beyond just cybersecurity cases. They could be used in law enforcement and national security to analyze crime patterns and predict potential threats.
- Challenges and opportunities in the field: The use of AI and big data in cybersecurity cases presents both challenges and opportunities. One of the challenges is the need for specialized expertise and resources to effectively implement these technologies. However, the opportunities are vast, including the potential to identify threats more quickly and accurately.
VII. Conclusion
In conclusion, the use of AI and big data projects can provide significant benefits for solving cybersecurity cases in law enforcement. Machine learning and big data can help identify patterns and trends that might be missed by traditional analytical methods. However, there are also ethical considerations that must be addressed, such as the potential for biases in machine learning algorithms and privacy concerns with the use of big data. As this field continues to evolve, there is a need for continued research and innovation, as well as legal and ethical frameworks to guide the use of these technologies.”