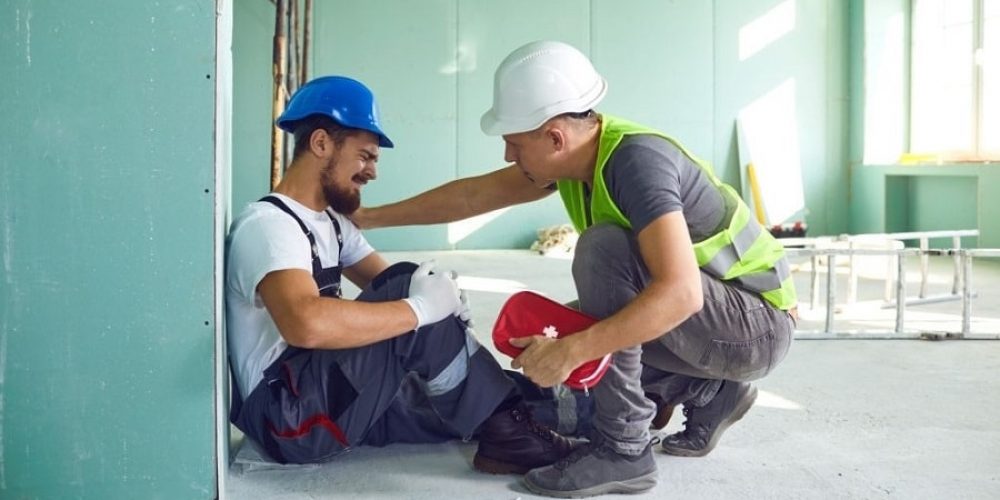
In case of a personal injury accident, determining the outcome of any claim or lawsuit is directly influenced by whose fault it was. In San Diego, establishing legal liability depends on the concept of negligence, which refers to the failure of the defendant party to exercise reasonable care, which has resulted in the injury of the plaintiff. With the help of a personal injury attorney, you can understand the general rules implemented to prove the fault, which would help you navigate the complexity of these cases.
- How to Determine Legal Liability?
The individual or party responsible for the injury is determined to be legally liable for the accident, as they were the ones who were less careful. However, in most personal injury cases, certain key principles are used to determine liability.
An individual is assigned the duty of care and is expected to exercise reasonable standards to prevent harm to others. If they fail to do so or cannot meet these standards, it is considered a breach of duty directly linked to the injury suffered by the other individual. This is termed causation, which leads to suffering or actual harm and loss of the injured party.
- When Multiple Parties Are at Fault?
It becomes complicated to determine the liability if multiple parties are involved in the accident. In this case, comparative negligence is applicable, where the degree of fault is measured for every party involved. The total damage is allocated based on a certain percentage, and the person with the highest rate is termed “at fault.” This proportion will also reflect on the compensation received by the victim party, even if they share a negligible fault in the incident. A personal injury lawyer from https://hhjtrialattorneys.com/ can help you get more insight into how the proportion distribution is made.
- Impact of the Injured Party’s Fault
The injured party’s compensation also gets affected if they are partially at fault for the accident. However, the rules vary based on the jurisdiction, such as:
- Pure Comparative Negligence allows recovery of damages, but their shared proportion of fault is subtracted from the total amount
- In modified Comparative Negligence, if the fault does not exceed a certain threshold, only the claim can be recovered, but at a reduced amount.
- Contributory Negligence, irrespective of the degree of fault, the victim is barred from recovering any damages if they share the liability.
- Exceptions to Liability
In personal injury law cases, certain exceptions are made to exempt a party from liability. If the injured person was unlawfully present on the property, then the property owner won’t be liable to pay for the injuries. Also, if the victim is engaged in any risky activity, it would also limit the defender’s liability.
Summing it Up
Establishing fault requires evidence, so you must collect accident reports, witness statements, photographs, videos, or expert testimonies. Other than this, to understand the general rules of personal injury cases, you must consult with a legal professional who can provide individual guidance based on the specific case you are trapped in.


Comments 0